Set your watch — we’ll cover all the PKI basics you didn’t know you didn’t know in less time than it takes to make a good cup of coffee
Have you recently made a purchase or shared other sensitive personal information with a website? If so, public key infrastructure likely had a hand in facilitating security for your internet transactions. Let’s dive right into what you need to know about PKI basics.
Public Key Infrastructure Explained: What Is PKI? A Look at the Basics
Public key infrastructure is the foundation of internet security and digital trust. It’s the rules, technical processes, and technologies that make it possible to exchange data securely on the internet. It relies on the use of public key infrastructure, which uses asymmetric cryptography (ie, public key cryptography) to protect sensitive data from unintended eyes. (More on asymmetric encryption is just a moment.)
Encryption is the process of taking plaintext (ie, readable) data and turning it into something indecipherable without the use of a secret key. On the internet, this involves using digital certificates that are issued by third-party certificate authorities (CAs). These publicly trusted entities must meet specific security standards to issue certificates.
What PKI Helps You Do
At its core, PKI enables you to do three important things (we’ll dive into the specifics of these more a little later):
- Authenticate entities you’ve never met (users, clients, servers, and other devices). The use of digital signatures helps you verify the other party’s identity, so you know you’re communicating with the right person or entity.
- Encrypt your data in transit (emails, files, and data transmissions). Public key encryption allows you to secure the data channel that you and the other party use to transmit data. This helps protect your data’s privacy and confidentiality by keeping it from prying eyes.
- Protect the integrity of your data (ensure no one secretly modifies data). Cryptographic hashes help you ensure that your data isn’t tampered with in transit.
Fundamentals of PKI: Asymmetric Cryptography Protects Data on Insecure Networks
Let’s take a closer look at PKI security fundamentals to understand how it’s used to secure data on the internet. Asymmetric cryptography relies on a public-private keypair:
- The public key encrypts data, and
- The private key decrypts it.
For you skimmers, here’s a quick overview of PKI basics in video form:
Up until the 1970s, encryption was always symmetric, meaning that one key would encrypt and decrypt data. This is why symmetric cryptography is also known as private key encryption (because it uses a single key instead of two unique ones). This means you’d have to physically meet up to exchange keys with someone to communicate via this private key encryption.
Obviously, this doesn’t work when you’re using the internet to do business with someone in another state, country, or continent. This is why asymmetric encryption came into the picture. Experts realized the need for exchanging sensitive key data even when only insecure (open) channels were available.
With public key cryptography, you don’t have to meet up in person because you’re using a cryptosystem that involves a public shared value and a private value. The sender uses the recipient’s public key to encrypt data, and then the recipient decrypts it using their corresponding private (secret) key. This enables the sender to give the recipient symmetric key information that both parties can use to create a secure, symmetrically encrypted session to communicate.
Asymmetric vs Symmetric Encryption
Here’s a quick overview of public key vs private key encryption:
Why bother using symmetric session? It’s because symmetric encryption is faster than asymmetric encryption, less resource intensive, and more secure when using smaller keys. But in order to get to a point where you can use symmetric encryption when connecting with someone in another geographic location, you first need to use asymmetric encryption to securely exchange data via open networks.
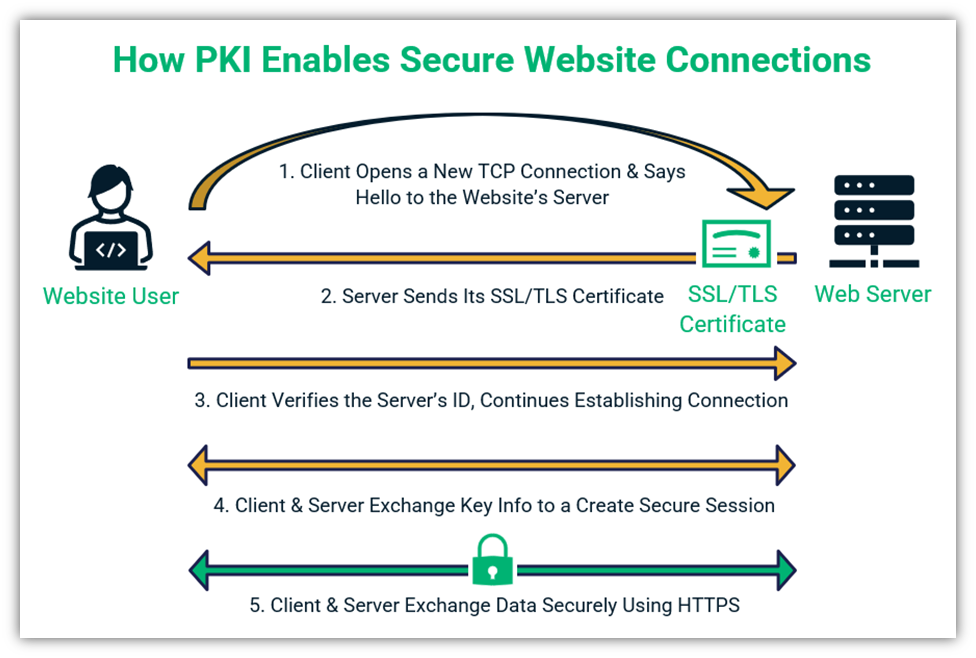
PKI Basics Example: How PKI Works to Create a Secure Website Connection
Let’s walk you through a basic overview of how it works when you connect to a website. This is known as an SSL/TLS handshake. In this process, your web client (browser):
- Verifies the site server’s digital identity using its SSL/TLS certificate. This ensures the client is connecting to the right place.
- Uses cryptographic processes (including encryption) to create a secure channel. This helps to protect your data as it transmits from your device to the website’s server.
- Protects the integrity of your data. This way, your recipient knows your data wasn’t tampered with or stolen in transit.
The process looks like this:
PKI Fundamentals: PKI Isn’t Just About Encryption
It also uses other types of cryptographic functions — and hashing ciphers and digital signature algorithms — to help with protecting data integrity and enabling identity verification.
- Hash function — This form of cipher is used to convert data of any size to a fixed-length string. Unlike encryption, which is a two-way function because encrypted data is intended to be reversed, hashing isn’t meant to be reverse engineered. It protects data integrity by informing you about whether data has been altered since it was signed. To learn more, check out our article on hashing vs encryption.
- Digital signature — A digital signature is what enables your device or operating system to identify an email, software executable, or another piece of data to determine whether it’s authentic (ie, came from the legitimate party, not an intruder).
These cryptographic processes play important roles in cyber security, including in the SSL/TLS handshake explained above.
Why You Should Use PKI for Your Organization
Aside from the reasons we’ve already covered (authentication, data integrity, and security), here are several other motivations for why you should use PKI to secure your organization and data:
- Secure access privileges at scale. Rather than relying strictly on traditional usernames and passwords, PKI digital certificates (ie, X.509 digital certificates) — particularly when paired with certificate life cycle management automation — help you secure access to your most sensitive resources and data more efficiently.
- Instill trust in your brand. People are more likely to want to do business with you if they can trust your business. Having a verifiable digital identity goes a long way in helping you earn that trust.
- Improve your Google ranking. If you didn’t know that enabling HTTPS on your website helps improve your search ranking, now you do. (You’re welcome.) So, if you want your website to have a chance of landing in Google’s top 10, then you need to install an SSL/TLS website security certificate on your server ASAP.
- Meet regulatory requirements. Even if they don’t necessarily mention PKI by name, many cybersecurity regulations and data privacy laws require the security, confidentiality, and data integrity protection PKI affords. This includes:
Final Thoughts on PKI Security Fundamentals
We hope that you’ve found this article on PKI basics informative and useful. It’s easy to see why PKI has been trusted as the foundation of internet security for decades. To learn more about various aspects of public key infrastructure, we invite you to go back and check out the resources embedded in the article.
Source
